Less than a month after Apple first shipped the iPhone in June 2007, a group called Independent Security Evaluators documented deep security design flaws in the device. Apple's most embarrassing flub: every iPhone application that Apple had written ran with so-called root privileges, giving each one complete control over the entire phone. Hackers found bugs in those apps that could be used to take over the phone from the inside. Apple didn't fix the design flaw until January 2008.
But after that rocky launch, Apple invested heavily in iPhone security. It's still possible for a hacker to take over a phone, but it's increasingly difficult, largely because each app runs in its own isolated "sandbox." The phone even verifies its operating system when it boots. Today the Apple iPhone 4S and iPad 3 are trustworthy mobile computing systems that can be used for mobile payments, e-commerce, and the delivery of high-quality paid programming—all of which bring Apple significant revenue in the form of commissions.
In fact, in its efforts to make its devices more secure, Apple has crossed a significant threshold. Technologies the company has adopted protect Apple customers' content so well that in many situations it's impossible for law enforcement to perform forensic examinations of devices seized from criminals. Most significant is the increasing use of encryption, which is beginning to cause problems for law enforcement agencies when they encounter systems with encrypted drives.
"I can tell you from the Department of Justice perspective, if that drive is encrypted, you're done," Ovie Carroll, director of the cyber-crime lab at the Computer Crime and Intellectual Property Section in the Department of Justice, said during his keynote address at the DFRWS computer forensics conference in Washington, D.C., last Monday. "When conducting criminal investigations, if you pull the power on a drive that is whole-disk encrypted you have lost any chance of recovering that data."
Mass-market cryptography hasn't been thought of as a potential threat to law enforcement since the "crypto wars" of the 1990s. Back then there was a very public battle against U.S. laws and regulations that limited the use and export of cryptographic technology. On one side, civil liberties groups and business interests said that the public needed strong cryptography to protect privacy and financial transactions. On the other side, law enforcement organizations warned that the same technology would empower drug dealers, kidnappers, money launderers, and terrorists.
Law enforcement lost the crypto wars: today there is essentially no restriction on mass-market cryptography. Fortunately, few of the predicted horribles came to pass. One reason is that the encryption systems developed and sold to consumers over the past 20 years have had an Achilles' heel: there has been no good way to let users securely manage encryption keys. Cryptography, for all its power, provides no security unless the keys used to lock the data remain secret.
Enter the iPhone. Apple's security architecture is so sturdy, and so tightly woven into its hardware and software, that it is both easy for consumers to use encryption on their phones and very difficult for someone else to steal the encrypted information.
At the heart of Apple's security architecture is the Advanced Encryption Standard algorithm (AES), a data-scrambling system published in 1998 and adopted as a U.S. government standard in 2001. After more than a decade of exhaustive analysis, AES is widely regarded as unbreakable. The algorithm is so strong that no computer imaginable for the foreseeable future—even a quantum computer—would be able to crack a truly random 256-bit AES key. The National Security Agency has approved AES-256 for storing top-secret data.
Apple did not respond to requests for comment on this story. But the AES key in each iPad or iPhone "is unique to each device and is not recorded by Apple or any of its suppliers," the company said in a security-related white paper. "Burning these keys into the silicon prevents them from being tampered with or bypassed, and guarantees that they can be access only by the AES engine."
What this means in practice is that when iOS devices are turned off, the copy of the encryption key in the computer's accessible memory is erased. That is why an investigator who gets a suspect's phone would have to try all possible keys—the task deemed impossible by the NSA.
The iPhone and iPad do keep a copy of the encryption key deeper in flash memory—otherwise there would be no way for the device to recover data when it was turned back on. But that encryption key is itself protected by the user's "PIN lock," a code that must be entered before the device can be used.
The iPhone always supported a PIN lock, but the PIN wasn't a deterrent to a serious attacker until the iPhone 3GS. Because those early phones didn't use their hardware to perform encryption, a skilled investigator could hack into the phone, dump its flash memory, and directly access the phone's address book, e-mail messages, and other information. But now, with Apple's more sophisticated approach to encryption, investigators who want to examine data on a phone have to try every possible PIN. Examiners perform these so-called brute-force attacks with special software, because the iPhone can be programmed to wipe itself if the wrong PIN is provided more than 10 times in a row. This software must be run on the iPhone itself, limiting the guessing speed to 80 milliseconds per PIN. Trying all four-digit PINs therefore requires no more than 800 seconds, a little more than 13 minutes. However, if the user chooses a six-digit PIN, the maximum time required would be 55 days; an eight-digit PIN would require more than 15 years. That's good enough for most corporate secrets—and probably good enough for most criminals as well.
"There are a lot of issues when it comes to extracting data from iOS devices," says Amber Schroader, CEO of Paraben, a supplier of forensic software, hardware, and services for cell phones. "We have had many civil cases we have not been able to process ... for discovery because of encryption blocking us."
Another iPhone innovation has to do with how and where data gets encrypted. Years ago encryption wasn't used very often because it was difficult to implement and computationally expensive—it took a lot of resources. Not so with the iPhone. Apple designed iOS devices so that the hardware that encrypts data is in the path the data travels when it moves from flash storage to the iPhone's main memory. This means that data can be automatically decrypted when read from flash into memory and reëncrypted when saved from memory back to flash. On the iPhone, encryption is essentially free.
That makes it possible to offer services like Foxygram, an iPhone app that allows users to share encrypted data in the knowledge that it cannot be intercepted and provided to law enforcement. Markus Kangas, cofounder of the app's creator, FoxyFone, says the goal is to "provide easy-to-use secure messaging for everyone and at the same time protect user privacy." He adds: "We are not there to police people."
Google's Android operating system also supports encrypted storage, but only for some of the data on the phone. More important, there is no key burned into the hardware, so even complex passwords can be broken by extracting them and using a network of a few hundred computers. BlackBerry phones, on the other hand, also have a strong encryption system that can be based on multiple factors in addition to the user's PIN.
But the BlackBerry system is designed for business customers and is harder to use than Apple's, which is made for the consumer market. Now that hardened, military-grade encryption is tough and easy for consumers to use—assuming the user has set a PIN lock that's both long and hard to guess—the nightmare scenario of the crypto wars may finally have come to pass.











 Tethering is the ability to share your mobile phone’s Internet connection with other devices such as laptops via the USB cable. When tethering is done over Wi-Fi, it’s called a wireless hotspot, a term I’m sure you are all familiar with. Since a typical household has more than one Internet capable device, sharing of Internet connectivity is a great way to reduce cost incurred by the ownership of multiple Internet connection. But as it happens, mobile data plans are usually expensive compared to broadband/ADSL plans. So you stand a better chance at saving if the sharing is made the other way round – that is, from the PC to the mobile device. If you have a wireless router at home and your mobile device supports Wi-Fi connectivity you are already set. But if any one of these key components is missing you will be unable to share your PC’s internet connection with your mobile. This is where reverse tethering comes in.
Tethering is the ability to share your mobile phone’s Internet connection with other devices such as laptops via the USB cable. When tethering is done over Wi-Fi, it’s called a wireless hotspot, a term I’m sure you are all familiar with. Since a typical household has more than one Internet capable device, sharing of Internet connectivity is a great way to reduce cost incurred by the ownership of multiple Internet connection. But as it happens, mobile data plans are usually expensive compared to broadband/ADSL plans. So you stand a better chance at saving if the sharing is made the other way round – that is, from the PC to the mobile device. If you have a wireless router at home and your mobile device supports Wi-Fi connectivity you are already set. But if any one of these key components is missing you will be unable to share your PC’s internet connection with your mobile. This is where reverse tethering comes in.




 The Pirate Bay is perhaps the most censored website on the Internet. Recently, a UK high court ordered several ISPs to block the website. Unfortunately, for the recording industry, the news about the forthcoming block was reported on the BBC resulting in a huge traffic spike of 12 million curious visitors in a single day. Similar incidents have occurred around other European countries and elsewhere as well. At present, the Pirate Bay remains blocked – partially - in Belgium, Denmark, Finland, India, Ireland, Malaysia, Netherland, China, and the UK.
The Pirate Bay is perhaps the most censored website on the Internet. Recently, a UK high court ordered several ISPs to block the website. Unfortunately, for the recording industry, the news about the forthcoming block was reported on the BBC resulting in a huge traffic spike of 12 million curious visitors in a single day. Similar incidents have occurred around other European countries and elsewhere as well. At present, the Pirate Bay remains blocked – partially - in Belgium, Denmark, Finland, India, Ireland, Malaysia, Netherland, China, and the UK. 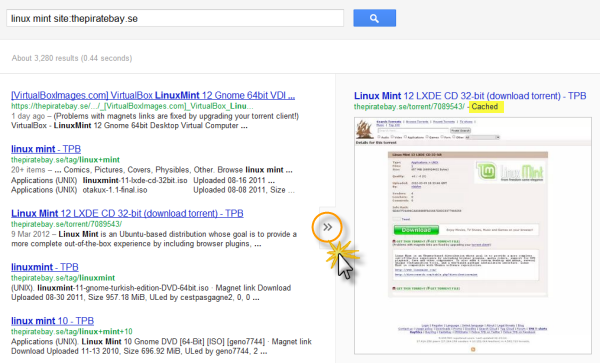

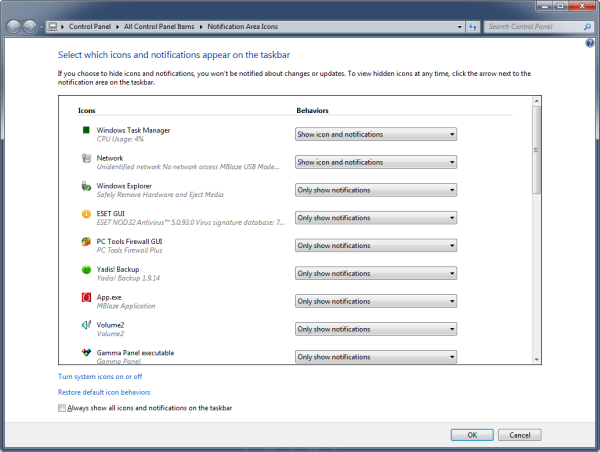
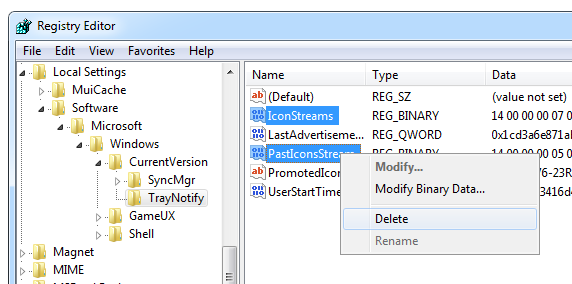


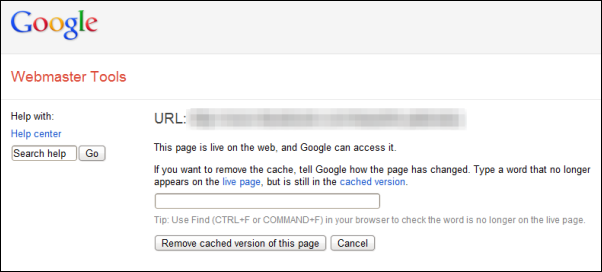

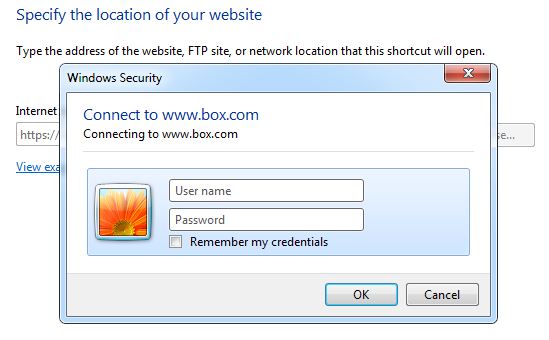
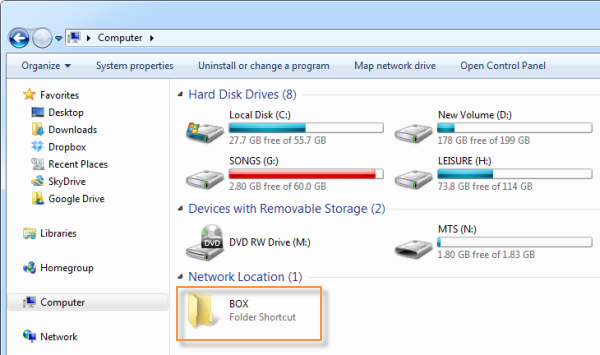
 With the recent launch of Google Drive and re-launch of Microsoft SkyDrive customers seeking for online file storage/backup solutions today have more choices than ever. However, “choice” is not the right word.
With the recent launch of Google Drive and re-launch of Microsoft SkyDrive customers seeking for online file storage/backup solutions today have more choices than ever. However, “choice” is not the right word.

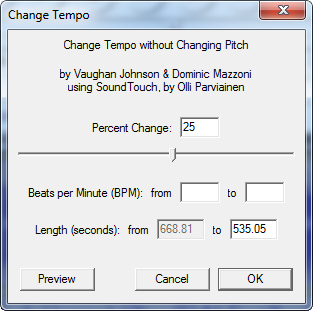
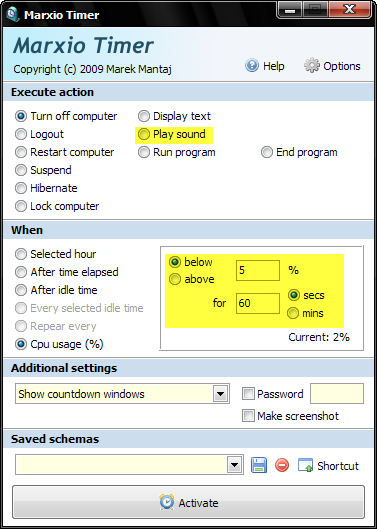
 Some programs require several minutes to process data. Usually anything that involves encoding and decoding requires time. File compression, video encoding/decoding, image processing take the most time to get done. Often we have to wait while these programs are processing data. We don’t exactly stare at the screen and twiddle our thumbs, instead we move to other programs that require our attention such as an unfinished Facebook game, but one way or the other, we wait.
Some programs require several minutes to process data. Usually anything that involves encoding and decoding requires time. File compression, video encoding/decoding, image processing take the most time to get done. Often we have to wait while these programs are processing data. We don’t exactly stare at the screen and twiddle our thumbs, instead we move to other programs that require our attention such as an unfinished Facebook game, but one way or the other, we wait.

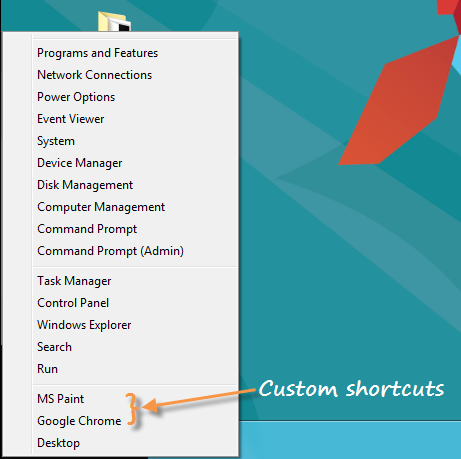
 Most of you know that Windows 8 doesn’t have the traditional start menu or the start button. Instead, you’ve got the start screen. There is but a second menu that is accessible by righting click on the lower-left corner of the screen. This context menu is called WinX menu because it can be launched by the keyboard shortcut Win+X.
Most of you know that Windows 8 doesn’t have the traditional start menu or the start button. Instead, you’ve got the start screen. There is but a second menu that is accessible by righting click on the lower-left corner of the screen. This context menu is called WinX menu because it can be launched by the keyboard shortcut Win+X.